Why Soil Waste Classification is Important
World Soil Day 2023
World Soil Day 2023.
Today 5th December 2023 is World Soil Day.
World Soil Day 2023 (WSD) and its campaign aim to raise awareness of the importance and relationship between soil and water in achieving sustainable and resilient agrifood systems. WSD is a unique global platform that not only celebrates soils but also empowers and engages citizens around the world to improve soil health.
Sustainable soil management practices, such as minimum tillage, crop rotation, organic matter addition, and cover cropping, improve soil health, reduce erosion and pollution, and enhance water infiltration and storage. These practices also preserve soil biodiversity, improve fertility, and contribute to carbon sequestration, playing a crucial role in the fight against climate change.
Our planet’s survival depends on the precious link between soil and water. Over 95 percent of our food originates from these two fundamental resources. Soil water, vital for nutrient absorption by plants, binds our ecosystems together. This symbiotic relationship is the foundation of our agricultural systems.
However, in the face of climate change and human activity, our soils are being degraded, putting excessive pressure on our water resources. Erosion disrupts the natural balance, reducing water infiltration and availability for all forms of life.
Background
World Soil Day (WSD) is held annually on 5 December as a means to focus attention on the importance of healthy soil and to advocate for the sustainable management of soil resources.
An international day to celebrate soil was recommended by the International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS) in 2002. Under the leadership of the Kingdom of Thailand and within the framework of the Global Soil Partnership, FAO has supported the formal establishment of WSD as a global awareness raising platform. The FAO Conference unanimously endorsed World Soil Day in June 2013 and requested its official adoption at the 68th UN General Assembly. In December 2013, the UN General Assembly responded by designating 5 December 2014 as the first official World Soil Day.
You can find out more about World Soil Day here
Key messages World Soil Day 2023
📌 Soil and water are essential resources for sustaining life on Earth.
- Soil and water provide the foundation for food production, ecosystems, and human well-being. Recognizing their invaluable roles, we can take proactive measures to safeguard these resources for future generations.
- Soil erosion and compaction disrupt the capacity of soil to store, drain and filter water, and exacerbates the risk of flood, landslides and sand/dust storms.
- Soil and water are the medium in which plants grow and obtain essential nutrients.
- Healthy soil plays a crucial role as a natural filter, purifying and storing water as it infiltrates into the ground.
- Rainfed agriculture systems account for 80 percent of croplands, contributing to 60 percent of the global food production. These systems rely heavily on effective soil moisture management practices.
- Irrigated agriculture systems withdraw 70% of the world’s freshwater and account for 20 percent of croplands.
📌 Soil and water are interconnected resources that need integrated management.
- The health of the soil and the quality and availability of water are interconnected.
- Implementing sustainable soil management practices enhances water availability for agriculture. Healthy soils, enriched with organic matter, play a crucial role in regulating water retention and availability.
- Efficient use of quality water, promoting the sustainable use of fertilizers and pesticides, employing appropriate irrigation methods, improving drainage systems, controlling pumping, and monitoring soil and groundwater salinity levels are essential to maintaining sustainable agricultural practices.
- Sustainable soil management is key to improve water productivity in irrigated systems.
📌 Improper soil and water management practices affect soil erosion, soil biodiversity, soil fertility, and water quality and quantity.
- Water scarcity leads to the loss of soil biodiversity, while leaching and eutrophication from agriculture practices lead to the loss of biodiversity in water bodies.
- The mismanagement of pesticides and fertilizers not only threatens soil and water quality but also poses significant risks to human health and ecosystems.
- Poor irrigation and drainage practices are some of the main drivers of soil salinization.
- Rising sea levels contribute to land loss, increasing the risk of soil salinization and sodification, which can negatively impact agricultural productivity.
📌 Soil and water conservation contribute to climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Improved soil and water management improves the land’s capacity to withstand extreme climate events such as droughts, floods and sand/dust storms.
- Integrated soil and water management practices provide essential ecosystem services, supporting life on earth and enhancing ecosystem resilience.
- Healthy soils act as a carbon sink, by sequestering carbon from the atmosphere, thus contributing to both climate change adaptation and mitigation efforts.
Correctly classifying Soil Waste during Construction Supports Healthy Soil Management.
At Earth Environmental & Geotechnical Ltd. we provide advice and geotechnical services to clients working on residential, commercial, industrial, renewable, infrastructure, and public sector projects, to name a few, on how to effectively manage soil waste on their development projects. Our services will ensure you are both compliant with legislation and efficient on when and how to reuse, recycle or dispose of soil waste.
Throughout the UK new developments can generate large amounts of soil waste as ground is excavated for foundations, basements, landscaping, etc. But what developers do with the excess soil can have a big impact on costs and legal compliance. At Earth Environmental & Geotechnical Ltd. we are frequently asked two important questions.
- How can I effectively manage the soil waste on the development site?
- What legislation covers soil waste?
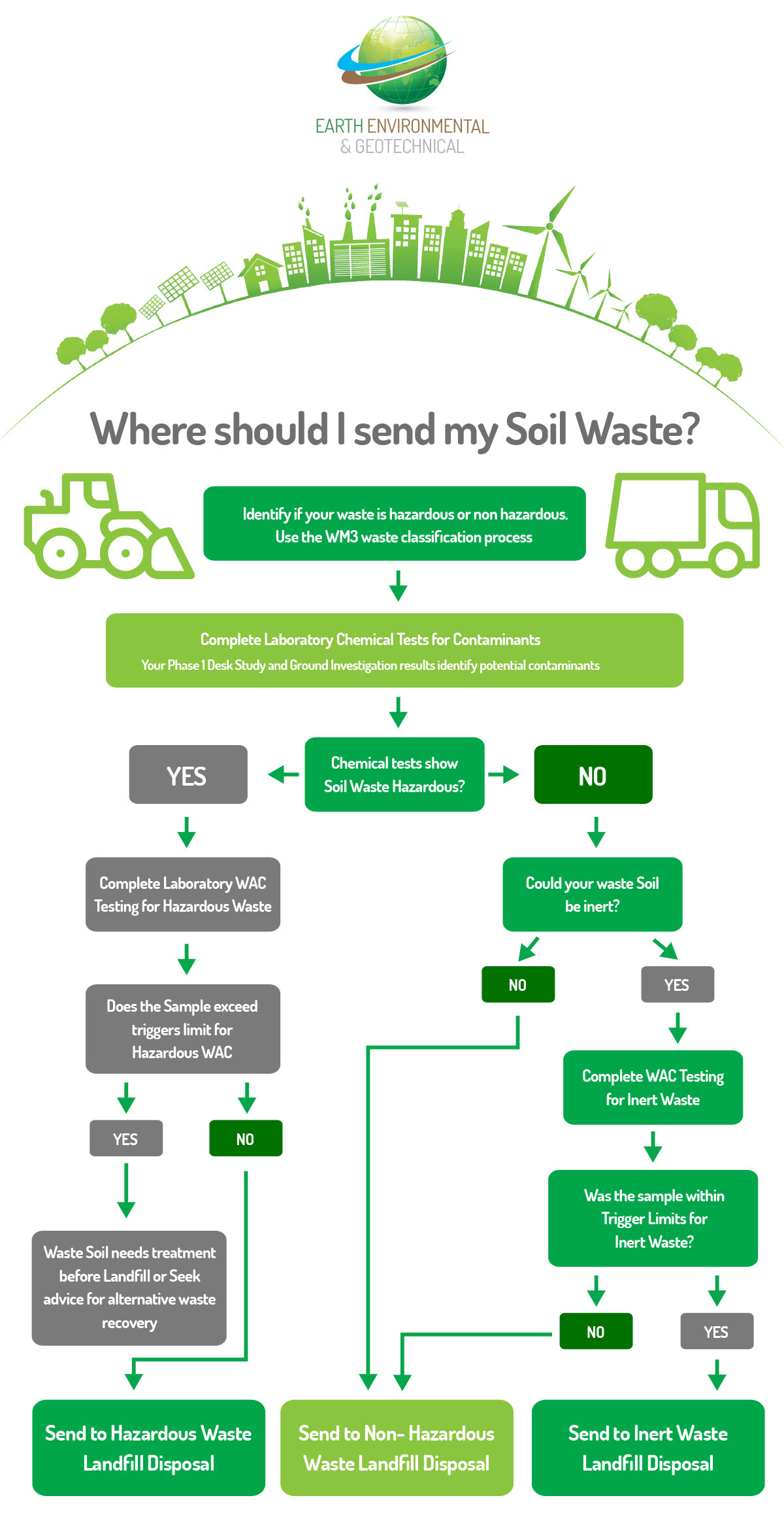
Soil Waste Classification is an essential process of construction projects, accurate segregation will reduce costs by minimising the volume of contaminated soil that is removed from the site. By correctly identifying and segregating the waste soil, it will reduce and control the risk of cross-contamination, resulting in reduced waste disposal costs and correct soil waste management can reduce the amount of waste disposed in hazardous landfill sites.
How can I effectively manage the soil waste on the development site?
You can find more information on our Soil Waste Classification Services here
The Construction Code of Practice developed to assist anyone involved in the construction sector to better protect the soil resources with which they work has detailed information. At Earth Environmental & Geotechnical we provide the full range of services highlighted in the code of practice so contact us now to discuss your development site.
A summary of the key messages in this Code of Practice is set out below:
Pre-construction planning
• Have a soil resource survey carried out on site by a suitably qualified and experienced soil scientist or practitioner at the earliest convenience and prior to any earthworks operations
• Incorporate the results of the soil resource survey into the site working strategy (e.g. Site Waste Management Plan or Material Management Plan) ensuring liaison between the soil resource survey and other ground investigations
• Ensure that you are informed of and follow waste regulations as necessary
• Consider the use of sustainable drainage systems on site as these can provide more long term protection of soils beyond the construction phase, by facilitating the infiltration and attenuation of surface water
Soil management during construction
• Prepare a Soil Resource Plan showing the areas and type of topsoil and subsoil to be stripped, haul routes, the methods to be used, and the location, type and management of each soil stockpile
• When stripping, stockpiling or placing soil, do so in the driest condition possible and use tracked equipment where possible to reduce compaction
• Confine traffic movement to designated routes
• Keep soil storage periods as short as possible
• Clearly define stockpiles of different soil materials
Landscape, habitat or garden creation
• Ensure that the entire soil profile is in a condition to promote sufficient aeration, drainage, and root growth
• Safeguard and utilise on-site soil resources where possible. If importing soils, use a reputable supplier, establish the source of the soil, and ensure it is suitable for the intended use
You can read the full document here
What legislation covers soil waste?
In England and Wales, any soil that is to be discarded or is required to discard is considered to be waste you can find out more information here
If waste soil is to be exported from the site, it must be classified in accordance with the guidance provided by the Environment Agency’s publication. The technical Guidance WM3 can be read here
You can find more information on waste classification here
Why Soil Waste Classification is Important World Soil Day 2023
Soil Waste Classification is Important
The correct process of soil waste classification can:
- Reduce the amount of material going to landfill
- Reduce the amount of material going to expensive hazardous landfill
- Reduce the amount of raw material brought onto the development site if waste can be reused
- Correctly identify any hazardous waste
- Reduce and control the risk of cross contamination, resulting in reduced waste disposal costs
- Provide mitigation steps for hazardous or contaminated soil waste
What is a Soil Waste Classification Test?
Soil waste classification testing is an first and most essential part of the waste disposal process. The Soil Waste Classification Test allows for the accurate classification of waste soil (hazardous or non-hazardous) and ensures appropriate management of waste. If a site is believed to be potentially contaminated, a soil waste classification test will be required prior to disposal of soil waste from site. A Phase 1 Desk Study combined with preliminary site investigations will identify potential contaminants to test for.
A soil waste classification test will analyse these contaminants and assess them against multiple waste regulations to determine whether soil waste is classified as hazardous or non-hazardous.
Soil waste classification testing may save you money by reducing disposal costs, if waste can be classified as non-hazardous, and avoiding potential penalties for wrongly disposing of soil waste.
What is The Difference between Soil Waste Classification Test and WAC Test?
Soil waste classification and WAC tests – (Waste Acceptance Criteria) are two important, and different steps in the waste management process on construction sites.
Waste Acceptance Criteria (WAC) testing is carried out to determine which landfill class soil waste can be sent to. WAC testing does not provide a measure of the total hazardous content of the soil, the tests are primarily by analysis of leachates derived from that waste.
As such WAC data must not be used for waste classification. WAC Testing is used to determine how a waste will behave once it’s buried in a landfill site.
If waste is identified as non-hazardous, through the waste classification testing process, it may be prudent to conduct WAC testing to confirm the soil waste meets inert landfill criteria. As inert landfill disposal is significantly cheaper than other landfill categories. We provide robust services to complete the soil waste classification on your development site and where identified complete the WAC test to ensure the most cost effective and eco responsible steps are taken to reuse, recycle or dispose of waste from your development site.