What is WAC Testing?
Environmental & Geotechnical Consultancy Services Throughout UK
Supported by Eight Regional Offices
How can I effectively manage the soil waste on the development site?
You can find more information on our Soil Waste Classification Services here
The Construction Code of Practice developed to assist anyone involved in the construction sector to better protect the soil resources with which they work has detailed information. At Earth Environmental & Geotechnical we provide the full range of services highlighted in the code of practice so contact us now to discuss your development site.
Please contact us early in the project development. We can ensure that the correct tests and site investigations are completed and where applicable provide mitigation steps to reduce the costs of managing contaminated land. Including possible options of: delineating the contaminated areas from non hazardous materials to reduce the waste needing to be disposed in expensive hazardous landfill, providing treatment of material to reduce contaminants.
Ideally disposal of waste should be the last resort and the correct risk assessments may identify that material can be reused onsite or at a different site with MMP – Material Management Plan.
Contact Us now to discuss
A summary of the key messages in this Code of Practice is set out below:
Pre-construction planning
• Have a soil resource survey carried out on site by a suitably qualified and experienced soil scientist or practitioner at the earliest convenience and prior to any earthworks operations
• Incorporate the results of the soil resource survey into the site working strategy (e.g. Site Waste Management Plan or Material Management Plan) ensuring liaison between the soil resource survey and other ground investigations
• Ensure that you are informed of and follow waste regulations as necessary
• Consider the use of sustainable drainage systems on site as these can provide more long term protection of soils beyond the construction phase, by facilitating the infiltration and attenuation of surface water
Soil management during construction
• Prepare a Soil Resource Plan showing the areas and type of topsoil and subsoil to be stripped, haul routes, the methods to be used, and the location, type and management of each soil stockpile
• When stripping, stockpiling or placing soil, do so in the driest condition possible and use tracked equipment where possible to reduce compaction
• Confine traffic movement to designated routes
• Keep soil storage periods as short as possible
• Clearly define stockpiles of different soil materials
Landscape, habitat or garden creation
• Ensure that the entire soil profile is in a condition to promote sufficient aeration, drainage, and root growth
• Safeguard and utilise on-site soil resources where possible. If importing soils, use a reputable supplier, establish the source of the soil, and ensure it is suitable for the intended use
You can read the full document here
What legislation covers soil waste?
In England and Wales, any soil that is to be discarded or is required to discard is considered to be waste you can find out more information here
If waste soil is to be exported from the site, it must be classified in accordance with the guidance provided by the Environment Agency’s publication. The technical Guidance WM3 can be read here
You can find more information on waste classification here
What is WAC Testing?
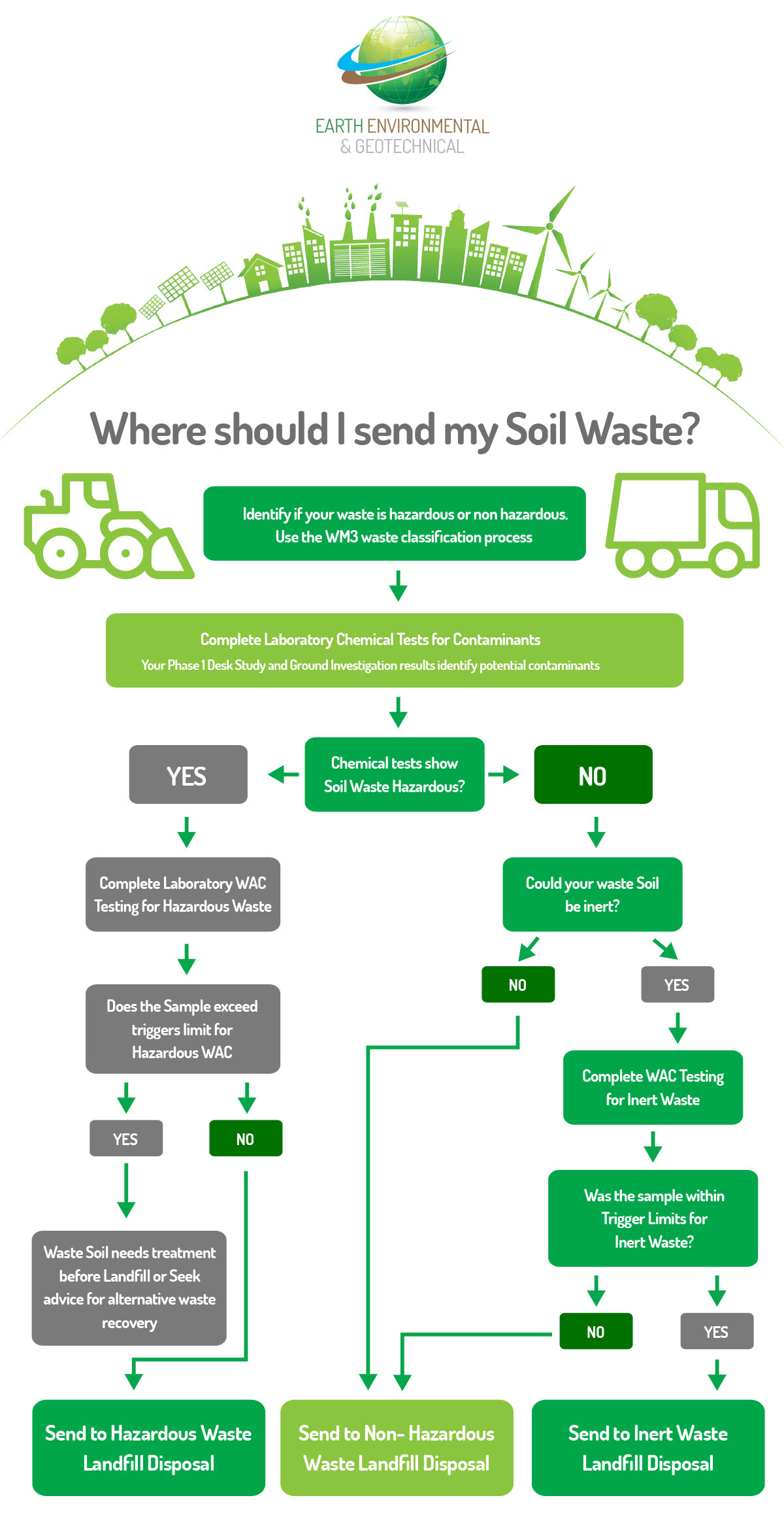
WAC Testing, also known as Waste Acceptance Criteria testing tells you which landfill site you can send your waste to.
WAC Testing sets out the criteria for the acceptance of waste at each landfill class, including criteria for underground storage. WAC testing is a legal requirement before a landfill can accept either inert or hazardous waste. Non-hazardous waste does not need WAC testing however if the waste could be inert it is prudent to complete WAC testing as inert landfill charges are more cost effective.
The WAC testing is the second step in the Soil Waste management process but can be completed in conjunction with The Soil waste Classification.
Both steps of the process are required. The soil waste classification will inform you what the waste is and the WAC test will inform you of where the waste can be sent.
What is the Process of Soil Waste Classification?
Waste soil classification is the process of characterising and categorising soil that could be discarded by disposal to landfill or reused on a different site. The process applies to all ‘excess’ soils even if it is not classed as contaminated by current or historic activity. Soil Waste Classification Testing is the first step in the waste disposal process.
The Environment Agency’s Technical Guidance document for the classification of waste is the WM3 Assessments.
Waste classification and assessment procedure
Stage 1 – Classify the Soil Waste
Classify the waste and identify its hazardous properties
You can find out more here
Stage 2 – is Waste Acceptance Criteria (WAC) testing.
When the List of Waste Codes has been determined WAC testing may be required.
There are four main landfill categories
- Inert
- Non-Hazardous
- Stable Non-Reactive Hazardous
- Hazardous
Waste classified as Hazardous in Stage 1 can only be deposited to either the Stable Non-Reactive Hazardous or Hazardous landfill. Non Hazardous waste can only be disposed of in an inert landfill site if a WAC test confirms this is appropriate.
Correct soil waste classification can save you money and reduce the amount of waste going to landfill.
Soil Waste Classification is an essential process of construction projects, accurate segregation will reduce costs by minimising the volume of contaminated soil that is removed from the site. By correctly identifying and segregating the waste soil, it will reduce and control the risk of cross-contamination, resulting in reduced waste disposal costs and correct soil waste management can reduce the amount of waste disposed in hazardous landfill sites.
Soil Waste Management.
Throughout the UK new developments can generate large amounts of soil waste as ground is excavated for foundations, basements, landscaping, etc. But what developers do with the excess soil can have a big impact on costs and legal compliance.
There is a big difference in cost between disposing constuction waste at an inert landfill or non hazardous landfill than a hazardous landfill. So having expert advice early in the project can save you time and money.
At Earth Environmental & Geotechnical Ltd. we provide advice and geotechnical services to clients working on residential, commercial, industrial, renewable, infrastructure, and public sector projects, to name a few, on how to effectively manage soil waste on their development projects.
Our services will ensure you are both compliant with legislation and efficient on when and how to reuse, recycle or dispose of soil waste.
Soil Waste Classification is Important
The correct process of soil waste classification can:
- Reduce the amount of material going to landfill
- Reduce the amount of material going to expensive hazardous landfill
- Reduce the amount of raw material brought onto the development site if waste can be reused
- Correctly identify any hazardous waste
- Reduce and control the risk of cross contamination, resulting in reduced waste disposal costs
- Provide mitigation steps for hazardous or contaminated soil waste